Laws of Reflection
Laws of Reflection: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Light, Reflection, Normal to the Plane Mirror & Ray of Light etc.
Important Questions on Laws of Reflection
What is the best explanation for why grass is green?
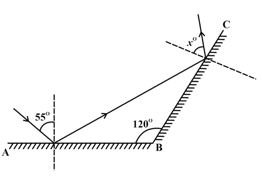
Observe the adjacent figure. AB and BC are two plane mirrors arranged at . A ray incident at angle at AB. Find the value of 'x'.
The angle of reflection is equal to angle of incidence when the light ray gets reflected from a smooth surface.
_____ is the phenomenon in which the right side appears to be left and left appears to be right in an image formed on the mirror.
Name the phenomenon in which the right side appears to be left and left appears to be right in an image formed on the mirror.
Give the name given to the phenomenon where the right side of an object appears to be the left side of the image in a plane mirror.
Light changes its _____ (direction/ speed/ frequency) when it is obstructed by any object, and it is called reflection.
The incident ray, normal and reflected ray all lie in different planes.
The incident ray, normal and reflected ray all lie in the same _____.
If an incident ray makes an angle of degree with a plane mirror, then the angle of reflection will be _____ degree.
If the angle of incidence is _____ the incident ray strikes the surface normally.
The angle between the reflected ray and the _____ is called the angle of reflection.
At the point of incidence, incident and reflected rays make _____ angle with the reflecting plane surface.
The ray that comes back from the surface after reflection is known as the _____ ray.
A non-luminous object can only be seen if the light
